
Geographically weighted regression (GWR)
Geographically weighted regression (GWR) is a useful tool for exploring spatial heterogeneity in the relationships between variables where non-stationarity is taking place on the space, that is where locally weighted regression coefficients move away from their global values. It allows us to understand changes in importance of different variables over space. In GWR, first appropriate bandwidth need to be selected for an isotropic spatial weights kernel, typically a Gaussian kernel with a fixed bandwidth chosen by leave-one-out cross-validation.
The basic form of the GW regression model is:
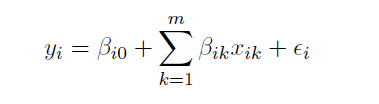
where yi is the dependent variable at location i; xik is the value of the kth independent variable at location i; m is the number of independent variables; Bi0 is the intercept parameter at location i; xik is the local regression coefficient for the kth independent variable at location i; and Ei is the random error at location i.
In this section we will cover: